'Toward a Feminist Poetics' by Elaine Showalter: Explained

'Toward a Feminist Poetics' is a groundbreaking essay by Elaine Showalter. The essay was first presented in 1978 as an introductory lecture on the first series on literature and women at University of Oxford. It was published in 1979. This seminal essay examines and questions the relationship between feminist literary theory and criticism, and the conventional literary theories. It is in 'Toward a Feminist Poetics' that Showalter first develops and coins the term "gynocriticism".
This blog aims to simplify the essay, and provides its key points and concepts.
Section I: Status of Feminist Criticism in the 1970s

In the very beginning of 'Toward a Feminist Poetics', Showalter refers to ‘Contemporary Approaches to English Study’. She highlights how all the contributions to it were made by men, including George Steiner, Raymond Williams, Christopher Butler, Jonathan Culler, Terry Eagleton, and Leon Edel, the biographer of Henry James. Showalter highlights that during the 1970s, out of all the critical approaches to literature and English studies, feminist criticism was the most secluded and least understood of all. Most proficient members of the English department were against it and as a result, never read it. Even when they read it, they did so with a prejudiced and stereotypical mindset. Showalter then proceeds to provide examples of such preconceived notions explicit among most critics during the 1970s.
She highlights Robert Partlow's perception of feminist criticism as “women’s lib propaganda masquerading as literary criticism”. Next, Showalter mentions Robert Boyers who wrote ‘A Case Against Feminist Criticism’ in Winter 1977 issue of Partisan Review. In it, Boyers assumed that feminist criticism will be “obsessed with destroying great male artists”. Interestingly, he based his comments on a single work by Joan Mellen titled ‘Women and Their Sexuality in the New Film’. For Boyers, feminist criticism was the “insistence on asking the same questions of every work and demanding ideologically satisfactory answers to those questions as a means of evaluating it”. Showalter describes Boyers’ response as intimidating, forcing women into adapt and mould themselves into a discourse that is more acceptable to academia. Expecting them to become stiff, rigid and indifferent to external stimuli.
Showalter observes that feminist criticism suffers such prejudice and attacks because it lacks a clear articulated theory. Even feminist critics are unaware what they mean to defend and profess.
Section II: Suspicion of Theory

Another obstacle in the way of feminist critical practice is the ‘suspicion of theory’. This suspicion of theory among feminist activists arises from the prevalent sexism among prominent theorists such as Harold Bloom, Robert Boyers, and Norman Mailer. It is significantly harder for feminists to rely on theory that's patriarchal. Most literary quarterlies of 1970s describe male experiences and perceptions and consider them to be universal. This suspicion of theory by feminist activists and theorists results in further isolation. Mary Daly in 'Beyond God the Father: Towards a Philosophy of Women's Liberation' writes:
“The God Method is in fact a subordinate deity, serving higher powers. These are social and cultural institutions whose survival depends upon the classification of disruptive and disturbing information as nondata. Under patriarchy, Method has wiped out women’s questions so totally that even women have not been able to hear and formulate our own questions, to meet our own experiences.” (Daly, p. 12-13)
Therefore, to a feminist need for authenticity, the academic demand for theory seems like an intimidating threat. This further marginalises feminist criticism.
Section III: Feminists' resistance to Academia
Where on one hand feminist critical theory is marginalised in academia, on the other hand, in the United States there is a resistance to being included in academia. Some believe that the activism and empiricism are the greatest strengths of feminist criticism, and that if the feminist critical theory is perfected and becomes a part of academia, the movement will die. Showalter suggests that this fear and resistance to include feminist theory in academia is a form of rationalization of the psychic barrier among women that has resulted due to their perpetual exclusion from theoretical discourse. Conventionally, women have always played the supporting role, whereas men have played the lead protagonist in the field of literary scholarship. While male critics in the twentieth century have openly established schools and coteries and have considered themselves as important as the writer, women have remained confined in the roles like that of translators, interpreters, hostesses, editors, etc.
This is why Showalter in 'Toward a Feminist Poetics' has outlined a brief classification of feminist criticism so that it can serve as an introduction to a literature that requires to be seen as a significant contribution of English studies. She also aims to reconstruct the political, social and cultural experiences of women.
Section IV: Woman as a Reader and Woman as a Writer


In 'Toward a Feminist Poetics', Showalter divides feminist criticism into two different categories – woman as a reader and woman as writer.
Woman as a reader or Feminist critique is the kind of feminist criticism where the woman consumes the literature produced by men. The supposition of female reader alters our grasp and understanding of a literary work as it makes us aware of the importance of its sexual codes. Showalter calls this kind of analysis of a literary work as a feminist critique. Just like other criticisms, it is founded on historical inquiry and explores ideological assumptions in literary texts. It studies the stereotypes of women in literature, the marginalization and misconceptions about women in criticism, and gaps in a male-constructed literary criticism and theory. Feminist critique also studies how women audience is manipulated and exploited in films and popular culture. It also analyzes woman-as-sign in semiotic systems.
Woman as writer or Gynocriticism is the second type of feminist criticism. Here, the woman creates the text and textual meaning, history, themes, genres and literary structures. This kind of feminist criticism studies the “psychodynamics of female creativity; linguistics and the problem of a female language; the trajectory of the individual or collective female literary career; literary history; and, of course, studies of particular writers and works.” Since there had not been any term exclusively for this kind of criticism, Showalter utilises the French term ‘la gynocritique’ or ‘gynocritics’
Difference between the feminist critique and gynocriticism
Feminist critique is a more political stream of criticism. It also has theoretical relations with Marxism and aesthetics. On the other hand, gynocriticism is more experimental and is self-contained. It is more connected to the other modes of feminist theory and research. Carolyn Heilbrun and Catharine Stimpson (editor of the journal Signs: Women in Culture and Society) compare feminist critique to the Old Testament that looks for the sins and the errors of the past. On the other hand, they compare gynocritics and gynocriticism to the New Testaments, seeking and depending on imagination. Both kinds of criticisms are essential for feminist vision.
Section V: The Mayor of Casterbridge by Thomas Hardy- an example of feminist critique

Showalter analyzes Thomas Hardy’s ‘The Mayor of Casterbridge’ through feminist critique. The very beginning of the novel where a drunk Michael Henchard sells his wife and infant daughter for as less as five guineas, is praised by the male critic Irving Howe in his work titled 'Thomas Hardy' (1968). To Howe, the beginning of the novel is brilliant. However, it would be different if the critic was a woman. According to Showalter, unless a woman has been trained/taught to ideologically identify with a male culture, she will have a different response and experience for the beginning of the novel. Howe describes Henchard’s wife as a “drooping rag” who is passive. However, no where in the beginning of the novel is she described as drooping. Through his critique, Howe indicates his fantasies as a male critic and in the process distorts the meaning of the text. Susan Henchard’s role is passive and and is further constrained by a female child. She has almost no second chances at life and has hardly any control in life. Male critics like Howe ignore that in the beginning of the novel, Henchard not only sells his wife but also his child who is a female. Henchard could only sell his child because she was a female since sons are seldom sold in patriarchal society. By selling his daughter and wife, Henchard is cutting himself off from the female community and completely including himself in male community. Henchard’s tragedy lies in realizing how insufficient a male community with its male code of paternity, money, and legal contract, is, and his inability to regain the love and warmth he eventually desperately needs.
The relation between Michael Henchard and his wife Susan Henchard are not the emotional center of the novel. It is rather his realization and appreciation of the strength and dignity of his daughter Elizabeth-Jane. Henchard is a self-proclaimed “women-hater” who feels nothing but condescending pity for womankind. He is eventually humbled and “unmanned” when he loses his position of mayor and his dignity. When Hardy shows Henchard as weak and vulnerable, he portrays the man at his best. “Thus Hardy’s female characters in The Mayor of Casterbridge, as in his other novels, are somewhat idealized and melancholy projections of a repressed male self”.
The above analysis of the novel is a feminist critique, and as we can see, it is an extremely male-oriented critique of a literary text. In 'Toward a Feminist Poetics', Showalter emphasizes that if we limit our study to stereotypical women, the sexist perception of male critics, and the confined role of women in literary history, we will never be able to learn about women’s experiences. We will only be able to know what men have taught women to be and feel. Feminist critique also tends to see women as natural victims by discussing it inevitably and obsessively. Additionally, there also exists celebration of seduction of betrayal, and the women being victims and seeing their victimization as opportunities. In order to understand women’s experience and emotions, we require help and training from male theorists such as Louis Althusser, Roland Barthes, Pierre Macherey, Jacques Lacan, etc, and learn the application of theory of signs and myths to male texts and films. Undergoing this intellectual exercise “increases resistance to questioning it, and to seeing its historical and ideological boundaries.”
Section VI: Gynocriticism and the Female Culture
Gynocriticism is different and in contrast to the fixation (negative or positive) on male literature. Gynocriticism creates a female framework to analyze women’s literature. It develops new models that are based on female experiences and sheds away male models and theories. Gynocriticism begins at the point when we free ourselves from the established male literary history, and stop attempting to adjust and fit women in male tradition. Gynocriticism instead focuses on a new world of female culture. Showalter says that :
“Gynocritics is related to feminist research in history, anthropology, psychology, and sociology, all of which have developed hypotheses of a female subculture including not only the ascribed status, and the internalized constructs of femininity, but also the occupations, interactions, and consciousness of women.”
Gynocriticism is not just confined to literature and history by men. Instead it is a feminist research in multiple fields that create a subculture exclusive to women. This subculture includes but goes beyond the established societal status of women and the conventional sense of femininity. It includes consciousness, interactions, and occupations of women. Michelle Z. Rosaldo in ‘Woman, Culture, and Society: A Theoretical Overview’ states that:
“ The very symbolic and social conceptions that appear to set women apart and to circumscribe their activities may be used by women as a basis for female solidarity and worth. When men live apart from women, they in fact cannot control them, and unwittingly they may provide them with symbols and social resources on which to build a society of their own.” (Rosaldo, p 39)
Similarly in literature, feminine values undercut and penetrate the very masculine system that contains them. For instance, women have utilized the myth of Amazon, and a secluded female society in many literary works and across genres from Victorian age to the contemporary science fiction.
Section VII: Prominent Feminist critics in Gynocriticism



Showalter further mentions groundbreaking work by young American feminist scholars who have provided new ways to understand the culture of American women in the 19th century and their literature through which it was mostly expressed.
The first work Showalter mentions is ‘The Female World of Love and Ritual’ by Carroll Smith-Rosenberg. It outlines the 19th century homosocial and emotional world through numerous archives of letters between women.
The second significant work Showalter mentions is ‘The Bonds of Womanhood: Woman’s Sphere in New England, 1780-1835’ by Nancy Cott. It emphasizes on the sisterly solidarity, loyalty, and shared experience among women that arises due to a legacy of submission and pain and cultural bondage.
The third work is ‘The Feminization of American Culture’ by Ann Douglas. This bold work by Douglas traces the origin of American mass culture found in sentimental literature of women and clergymen that were “two allied and “disestablished” post industrial groups.
All the three works mentioned above are by social historians.
The fourth significant work is by Nina Auerbach titled ‘Communities of Women: An Idea in Fiction’. The work explores female bonds through women’s literature- from the matriarchal households found in the works of Louisa May Alcott and Elizabeth Gaskell, to the schools and colleges for women found in the works of Dorothy Sayers, Sylvia Plath, and Muriel Spark. Such works that are based on English women are extremely significant and urgently required. There is no dearth of sources for research as there is an abundance of manuscripts that are undiscovered.
Section VIII: Importance of a female tradition and women's experiences

Showalter says that gynocriticism must consider political, social, and personal histories while studying women’s literary choices and careers. Virginia Woolf in her essay 'Women and Fiction' (1929) writes that “In dealing with women as writers, as much elasticity as possible is desirable; it is necessary to leave oneself room to deal with other things besides their work, so much has that work been influenced by conditions that have nothing whatever to do with art.”
As an example Showalter mentions the case of ‘Aurora Leigh’ by Elizabeth Barrett Browning. In the novel’s introduction, Cora Kaplan discusses the writer’s intellectual milieu and defines her feminism as romantic and bourgeois, one that depends upon the transforming powers of art, love, and Christian charity. However, Kaplan misses the discussion of one male poet who must had the biggest influence on her work in the 1850s- Robert Browning. Since we are aware how vulnerable women are to the established value system and aesthetics of male tradition, and to male approval, we must also be receptive to the marriage between two artists. Marriage between two writers or artists in most cases amounts to internal conflicts and eventually complete self-erasure for women. This is visible in Barrett Browning’s letters of 1850s addressed to Mrs. David Ogilvy. In 1854, she writes to her friend:
“I am behind hand with my poem…Robert swears he shall have his book ready in spite of everything for print when we shall be in London for the purpose, but, as for mine, it must wait for the next spring I begin to see clearly. Also it may be better not to bring out the two works together…If mine were ready I might not say so perhaps.”
Browning’s letters display a very familiar struggle between her own ambition and commitment to her work and her love and ambition for her husband. In a way, she wants her husband to be more successful, to be the better writer.
Therefore, without a complete understanding of the “framework of the female subculture”, we are bound to misunderstand and misread the themes and structures of women’s literature. We might also be unable to establish important connections within a tradition.
Section IX: The pain of feminist awakening
Florence Nightingale, in a passage from her essay 'Cassandra' in 'The Cause: A History of the Women's Movement in Great Britain', considers the pain and discomfort of feminist awakening as its very essence and causes progress and guarantee of free will. She protests against the complacent lives of middle class Victorian women and states:
“Give us back our suffering, we cry to Heaven in our hearts--suffering rather than indifferentism--for out of suffering may come the cure. Better to have pain than paralysis: A hundred struggle and drown in the breakers. One discovers a new world.” (p. 398)
Waking up from the pleasant and comfortable sleep of the Victorian womanhood was naturally painful. As evident in the works of George Eliot, Edith Wharton, Kate Chopin, and Olive Schreiner, women wake to a world where they cannot become what they aspire to be, and rather than struggling, they die. Female suffering is consumed by both men and women as a literary commodity. The fulfilment in the plots of many significant novels such as ‘The Mill on the Floss’, ‘The Story of an African Farm’, and ‘The House of Mirth’ occurs when a male mourner visits the grave of a heroine.
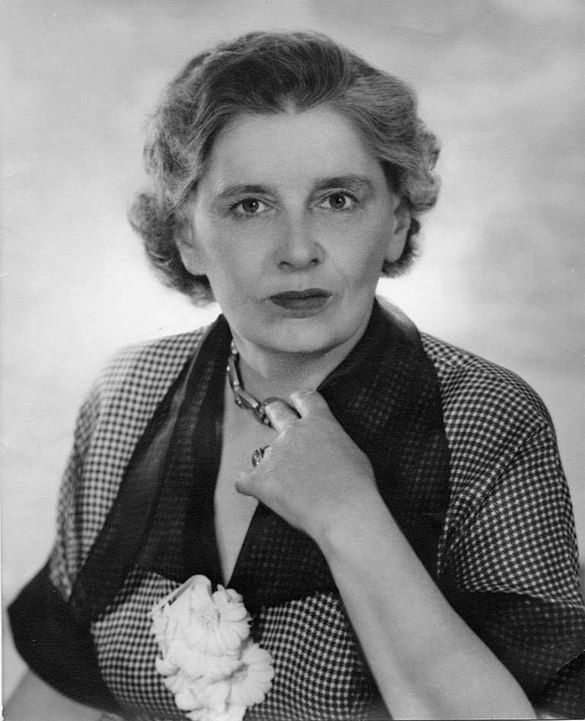

Even for Dame Rebecca West in 'And They All Lived Unhappily Ever After' (1974), misery and unhappiness are still a central theme of contemporary fiction by English women. For instance, in ‘Down Among the Women’ and ‘Female Friends’ by Fay Weldon, suicide by the heroine becomes like a domestic accomplishment. Similarly, ‘The Driver’s Seat’ by Muriel Spark is a desperate attempt of the heroine “to hunt down a woman-hating psychopath and persuade him to murder her”. The protagonist, Lise, selects the dress she wanted to be murdered in, patiently pursues her assassin and gives him the knife. Through this, Spark provides us with significant feminine wisdom: “that a woman creates her identity by choosing her clothes, that she creates her history by choosing her man.” She further questions if the woman’s only form of self-assertion is to select her destroyer, and whether it is the man or the woman who is in the driver’s seat. If we assume the violence of these self-destructive novels as neurotic expressions of some personal pathology, we would be ignoring the possibility that these worlds and circumstances might be true. We might be ignoring according to Annette Kolodny:
“...the possibility that the worlds they inhabit may in fact be real, or true, and for them the only worlds available, and further, to deny the possibility that their apparently “odd” or unusual responses may in fact be justifiable or even necessary.”
Showalter emphasizes that women’s literature should rise above death, suffering, madness, and compromises. However she asserts that initial suffering is inevitable to discover a new world and life. Some recent literature by women has begun to place the transformational pain to history. Adrienne Rich is one such female writers whose writings explore the will to change. Her book ‘Of Woman Born: Motherhood as Experience and Institution’ challenges and questions the rejection and alienation of the mothers by their daughters due to patriarchy. The literature in the past have commonly dealt with the fear of becoming one’s own mother or “matrophobia”. Hatred towards her mother was like a feminist enlightenment for a woman. However, women’s literature of the 1970s, attempts to recover from matrophobia like in ‘Surfacing’ by Margaret Atwood, and 'Kinflicks' by Lisa Alther. Just like the death of the father used to be a significant event in a male protagonist’s life, a mother’s death in the life of a female protagonist is now treated with the same gravity and profundity in female literature. Studying these changes and awakenings and new mythologies of female culture are one of the major tasks of gynocriticism.
Section X : Women and the Novel: The “Precious Speciality”
One of the most consistent and significant assumption of feminist reading is that various women’s experience will be expressed through a specific and distinctive genres and forms in art. While exploring the meaning of women’s literature and its future, Victorian reviewers such as G.H. Lewes, Richard Hutton, and Richard Simpson focused on “educational, experimental, and biological handicaps of the woman novelist..". Women, too shared this perception. According to the novelist Fanny Fern, women had been allowed to write novels in order to harmlessly channel their frustrations and fantasies that would have otherwise threatened a conventional family, church, and the state. It was a safe outlet for women living a stifling and loveless life. She urged women to write their deepest thoughts and desires so that when they have long gone, and their works are found by either their husband or their father, they would realise, they hardly knew their wife or daughter. It must be noted that although Fern’s writing was fierce, she was completely controlled by her need to provoke a masculine response. During the end of the 20th century, Women Writers Suffrage League had begun to examine the mental bondage of women’s literature to a male dominated publishing industry. The first president of Women Writers Suffrage League, a novelist, and an actress, Elizabeth Robins had argued that no female writer had been free of the mental bondage to truly explore a female consciousness. In 'Woman's Secret' Robins states:
"The realization that she had access to a rich and as yet unrifled storehouse may have crossed her mind, but there were cogent reasons for concealing her knowledge. With that wariness of ages which has come to be instinct, she contented herself with echoing the old fables, presenting to a man-governed world puppets as nearly as possible like those that had from the beginning found such favour in men’s sight.
Contrary to the popular impression, to say in print what she thinks is the last thing the woman-novelist or journalist is so rash as to attempt. There even more than elsewhere (unless she is reckless) she must wear the aspect that shall have the best chance of pleasing her brothers. Her publishers are not women.”
In order to combat this prevailing male dominance in the publishing industry of the 19th century, many women organized publishing houses- beginning with Victory Press of Emily Faithfull that was established in 1870s. The Women Writers Suffrage League believed that once the male domination is overthrown, all the undocumented and marginalized female psyche will find its distinct literary expression. Writers like George Eliot and Virginia Woolf firmly believed that literature produced by women had a promise of distinctly female vision and a “precious speciality”.
Section XI: Feminine, Feminist, Female
This section of 'Toward a Feminist Poetics' focuses on the three stages of Feminine, Feminist, and Female in feminist criticism. According to Showalter in her book ‘A Literature of Their Own’, Feminine, Feminist, and Female are three themes or stages of the feminist literary criticism of the 1960s and 1970s.
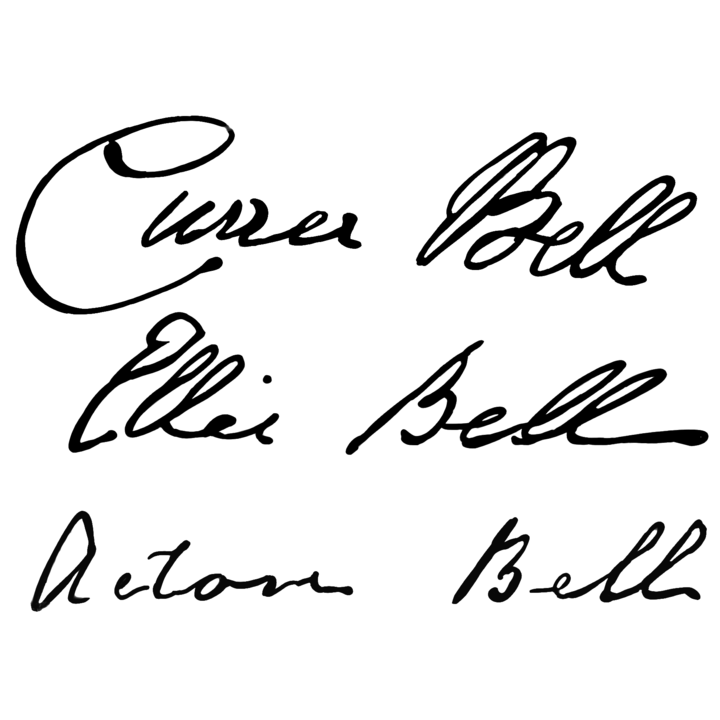
The feminine phase in the feminist literary criticism was around the years 1840 to 1880. During this stage, women wrote mainly in order to compete with male writers. They constantly compared their intellect to that of the male writers and had internalized perceptions about female nature. One of the distinct characteristic of this phase is adoption of a male pseudonym by many female writers- George Eliot, Currer Bell, Acton Bell, and Ellis Bell, etc. This male pseudonym was not just a name, it impacted the tone, characterization, structure of the novel. Adopting the male pseudonym also indicated how women were aware about the liabilities of being a female author in a male dominant literary world.
While English women adopted male pseudonyms, American writers adopted extremely feminine pseudonyms such as Fanny Fern, Fanny Forester, Grace Greenwood, etc. Behind these little-me names were hidden professional skills and boundless energy of women writers. There also existed female writers who created an illusion of a male writer with an encoded domestic message of femininity. An example of such writer is Harriet Parr, a victorian novelist who wrote under the pen name of Holme Lee. The literature produced during this phase is usually oblique, subversive, ironic, and displaced, and one needs to read between the lines to catch any missed meanings or possibilities in the text.

The feminist phase in the feminist literary criticism spans through the years 1880 to 1920. Women during this phase reject the traditional perceptions of femininity. Through literature, they emphasize and dramatize the experiences of all the injustice and wrongs done to women. Female novelists belonging to this phase such as Elizabeth Gaskell and Frances Trollope express a personal sense of injustice through their novels of class struggle and factory life. Writers of the feminist phase redefine the role of a female artist in terms of responsibility towards suffering sisters. Typical works belonging to this phase are the Amazon utopias of the 1890s. They include perfect societies by women set in future America or England that are explicitly against the male government, laws and medicine. One such author belonging to the Amazon utopia is Charlotte Perkins Gilman. She examines the obsession of masculine literature with war and sex, and explores the possibilities of feminist literature free of such elements. Gilman carries the idea of “precious speciality” introduced by Eliot to its matriarchal extremes. She compares her perception of sisterhood to that of a beehive in 'The Man-made World: or, Our Androcentric Culture'. Gilman writes:
“...the bee’s fiction would be rich and broad, full of the complex tasks of comb-building and filling, the care and feeding of the young…It would treat of the vast fecundity of motherhood, the educative and selective processes of the group-mothers, and the passion of loyalty, of social service, which holds the hives together”
The feminist phase was a Feminist Socialist Realism with a vengeance. However, female writers could not be limited to maternal topics and similar didactic formulas.
The Female phase has been ongoing since the 1920s. In this phase of feminist literary criticism, women reject imitation as well as the protest of male literature, which was in both cases a form of dependency. Instead, they turn their focus to female experience for source of art that is free of the male influence and control. They offer a feminist analysis of forms and techniques of literature. Virginia Woolf and Dorothy Richardson are the representatives of the female phase of the feminist literary criticism. They think in terms of male and female sentences and also divide their work into “masculine” journalism and “feminine” fictions. Additionally, they redefine and sexualize external and internal experiences.
Showalter suggests that all three phases of feminist literary criticism are significant and it is extremely significant to approach them with historical awareness. We must reconstruct the past and rediscover large amount of literature – novels, poems, plays – by women that have been ignored. We must build a continuous female tradition spanning “from decade to decade, rather than from Great Woman to Great Woman.” Once we create a timeline of literary tradition, we will be able to see the “patterns of influence and response from one generation to the next, we can also begin to challenge the periodicity of orthodox literary history and its enshrined canons of achievement.” Showalter further stresses that since we have always studied female literature in isolation, their literary connection and tradition has escaped us. However, if we begin to go beyond Austen, Brontës, Eliot, and begin to read hundreds of ignored works written by fellow female writers, we are bound to discover patterns and phases in the evolution of a female tradition that reflect the developmental phases of any subcultural art.
Section XII: Feminist Criticism, Marxism, and Structuralism
While creating a tradition, feminist criticism refers to various theories, and also revises and subverts prominent theories and ideologies, specially Marxist aesthetics and structuralism. It also attempts to alter their vocabulary and methods in order to make them inclusive of gender. However, Showalter believes that this is still not satisfactory, and that feminist criticism cannot always survive upon “men’s ill-fitting hand-me-downs”. Instead, they must free themselves from the established terminologies and methods and create and analyse art through their own impulses. This is what gynocriticism attempts to do. However, it does not imply that feminist criticism needs to reject all professional literary terms. The historical conditions under which critical ideologies are created are the reason why their feminist adaptations have reached a dead-end. Both Marxism and Structuralism are considered significant and elite critical approaches. “Science” is a key element in both the critical approaches. Both Marxism and Structuralism are considered to be the “sciences of the text”. Both the theories consider the author to be a producer of the text that is determined by historical and economical factors, rather than a creator. Structuralism too deals with the science of meanings, a grammar of genres.
Theories like Marxism and Structuralism did not rise to prominence accidentally. The era around the year 1950s was the time of scientific competition, when a lot of money flowed into laboratories and research. This was also the time when male humanist academia was at its lowest. Northrop Frye in his 1957 ‘Anatomy of Criticism’ presented the very first idea of a systematic critical theory that could help literary studies attain qualities of science. Thus, the new sciences of the text that were based on linguistics, structuralism, deconstructionism, neoformalism, psychoaesthetics, etc, gave literary critics the chance to show that their work too could be and was as aggressive and masculine as nuclear physics. In this process it excluded the notion that literary studies could be intuitive, expressive, and feminine.
Showalter very accurately observes that
“Literary science, in its manic generation of difficult terminology, its establishment of seminars and institutes of postgraduate study, creates an elite crops of specialists who spend more and more time mastering the theory, less and less time reading the books. We are moving towards a two-tiered system of “higher” and “lower” criticism, the higher concerned with the “scientific” problems of form and structure, the “lower” concerned with the “humanistic” problems of content and interpretation.”
This higher and lower criticism eventually assume subtler gender identities and assume sexual polarity. According to Showalter a synthesis between feminist literary theory and Marxism and Structuralism, but is just a one-sided exchange. While scientific literary theories attempt to get rid of the subjective, feminist criticism asserts the ‘Authority of Experience’. Women’s experience can easily vanish, become mute, invisible, or get lost in diagrams of theories likes structuralism, and the class conflict of Marxism. We must fiercely protest against the equation of feminine with the irrational. We must also recognize that questions that must be asked the most-such as repressed messages of women in history, psychology, anthropology-- cannot be answered by science.
According to Showalter the dead end in feminist literary criticism goes beyond the lack of appropriate definitions and terminologies. It arises from our own divided conscience.
“We are both the daughters of the male tradition, of our teachers, our professors, our dissertation advisers, and our publishers-a tradition which asks us to be rational, marginal, and grateful; and sisters in a new women's movement which engenders another kind of awareness and commitment, which demands that we renounce the pseudo-success of token womanhood and the ironic masks of academic debate.”
It is rather comfortable to continue to stick to the male dominated academics and theory and to be the teachers, anthropologists, psychologists, and critics of male literature, while considering to be universal. However, we must not under any circumstance become complacent and must continue to accept this intellectual challenge. We must rewrite anatomy, rhetoric, poetry and history.
Towards the end of 'Toward a Feminist Poetics', Showalter concludes,
“The task of feminist critics is to find a new language, a new way of reading that can integrate our intelligence and our experience, our reason and our suffering, our skepticism and our vision. This enterprise should not be confined to women. I invite Criticus, Poeticus, and Plutarchus to share it with us. One thing is certain: feminist criticism is not visiting. It is here to stay, and we must make it a permanent home.”
'Toward a Feminist Poetics' by Elaine Showalter
Summary and Overview
'Toward a Feminist Poetics' by Elaine Showalter : a Summary
- Feminist literary criticism was marginalised and most prominent literary critics of the 1970s were prejudiced against it. This was because feminist theory was not articulate.
- Suspicion of theory is another factor that prevents the development of feminist critical practice. Since literary theory has always been patriarchal, feminist critics are unable to comfortably rely on it. This isolates feminist theory even further.
- Many feminist critics in the United States believe that the inclusion of feminist theory in male dominant academia will deprive it of its very essence
- Showalter categorizes feminist criticism into woman as a reader, and woman as a writer. Woman as a reader or feminist critique focuses on literature written by men. It highlights the stereotypical perception of womanhood and explores traditional ideological assumptions in literary works by men. On the other hand, woman as a writer or gynocriticism focuses on woman as a writer where she is the one who creates the text, history, meaning, etc.
- 'Toward a Feminist Poetics' examines Thomas Hardy's The Mayor of Casterbridge through feminist critique. Showalter shows how feminist critique focuses solely upon the conditions and treatment of women with respect to men. She points out that if we continue to do so, we will never be able to shift our focus to women's experiences without a masculine influence.
- In contrast to the male obsessed feminist critique, gynocriticism goes beyond and attempts to create a tradition of women's experiences, literature, and theory free of conventional assumptions.
- Showalter provides examples of gynocriticism through the works of Carroll Smith-Rosenberg, Nancy Cott, Ann Douglas, and Nina Auerbach.
- Women's literature must be read and studied in relation with their personal history, political, and social situation. Showalter provides an example through Cora Kaplan's review about Elizabeth Barrett Browning's 'Aurora Leigh'. She emphasizes how Kaplan completely ignores the factor that must have impacted Browning's writer the most– her relationship with her husband, Robert Browning, who himself was a celebrated writer.
- Showalter mentions how Florence Nightingale considers the pain and suffering of feminist awakening a guarantee of new change and progress. Female suffering has always been a popular literary commodity, and many significant and popular works have included it in their plots. However, Showalter suggests that women's literature must not stay confined to the themes of death, madness, and suffering, and must go beyond it.
- Since the publishing industry was male dominated too, women could not write anything without being free of mental bondage to get appreciation or acceptance from a male publisher. According to Showalter, only when all such mental barriers are removed, will women be able to create a literature with a distinct and 'precious speciality'.
- 'Toward a Feminist Poetics' by Showalter also refers to the three phases or stages of feminist literary criticism. The first phase is the feminine phase where women aimed to compete with male writers, and compared their craft with that of their male contemporaries. The second phase is the feminist phase where the critics focus on the injustices and wrongs done to women in literary texts, and reject the conventional roles of females. Finally, the female phase is independent of the dependency on and obsession with the male literature. It instead aims to focus on creating a female literary tradition that includes women's internal experiences and personal history.
- Showalter further talks about how feminist literary criticism and theory has reached a dead-end despite interacting with prominent theories such as Marxism and Structuralism. These theories constitute a higher criticism that is considered professional and scientific, while the subjective and humanistic feminist criticism is either excluded or is seen as lower criticism. Feminist criticism realises that we are the products of both, a male dominated literature, theory, academia, and publishing, and a new female movement that accepts the intellectual challenge of rewriting history, poetry, and rhetoric according to women's intellect, experience, suffering, and vision.
References
Barry, Peter. Beginning Theory : An Introduction to Literary and Cultural Theory. 1995. 4th ed., Manchester, Manchester University Press, 2017.
Charlotte Perkins Gilman. The Man-Made World, or Our Androcentric Culture, by Charlotte Perkins Gilman. London, T. Fisher Unwin, 1911.
Daly, Mary F. Beyond God the Father: Toward a Philosophy of Women’s Liberation. Boston, Beacon Press, 1973. (p. 12-13)
Diamond, Arlyn, and Lee R Edwards. The Authority of Experience. Amherst : University of Massachusetts Press, 1977.
Elizabeth Barrett Browning. Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s Letters to Mrs. David Ogilvy. Quadrangle/The New York Times Book Company, 1973.
Michelle Zimbalist Rosaldo, et al. Woman, Culture, and Society. Stanford, Calif., Stanford University Press, , Printing, 1974. (p. 39)
Showalter, Elaine. A Literature of Their Own : British Women Novelists from Bronte to Lessing. London Virago, 1978
Showalter, Elaine. The New Feminist Criticism. New York : Pantheon, 1985.